Blog

Laser hair removal has gained immense popularity as a long-term solution for unwanted hair, particularly in sensitive areas like the bikini line. This method is not only efficient but also offers a level of precision that traditional hair removal methods often lack. In this blog, we'll explore how laser hair removal works, its benefits, and what you can expect during the process. How Laser Hair Removal Works Laser hair removal uses concentrated light beams to target and destroy hair follicles. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process: 1. Consultation and Patch Test: Before undergoing treatment, a consultation with a licensed practitioner is essential. They will assess your skin type, hair color, and the specific area to be treated. A patch test may also be performed to check for any adverse reactions. 2. Preparation: On the day of the procedure, the area will be cleaned, and a topical anaesthetic may be applied to minimise discomfort. Protective eyewear is also provided to shield your eyes from the laser. 3. Laser Application: The practitioner uses a handheld laser device to emit light energy into the hair follicles. The pigment in the hair absorbs this energy, which damages the follicle and inhibits future hair growth. The process is quick, often taking only a few minutes for the bikini area. 4. Post-Treatment Care: After the session, you may experience some redness or swelling, similar to a mild sunburn. Applying soothing aloe vera or ice packs can help alleviate discomfort. It's crucial to avoid sun exposure and follow any aftercare instructions provided by your practitioner. Benefits of Laser Hair Removal - Long-lasting Results: Unlike shaving or waxing, laser hair removal offers long-term hair reduction. Many patients experience a significant decrease in hair growth after just a few sessions. - Precision: The laser targets dark, coarse hairs while leaving the surrounding skin undamaged, making it ideal for sensitive areas like the bikini line. - Speed: Each pulse of the laser takes only a fraction of a second, allowing for quick treatment sessions. The bikini area can often be treated in under 30 minutes. - Less Ingrown Hairs: Traditional hair removal methods can lead to ingrown hairs, but laser hair removal significantly reduces this risk, providing a smoother skin appearance. What to Expect - Number of Sessions: Most people require multiple sessions (typically 6 to 9) spaced about 4 to 6 weeks apart to achieve optimal results. The exact number will depend on your hair growth cycle and individual response to treatment. - Pain Level: While discomfort varies from person to person, many describe the sensation as similar to a rubber band snapping against the skin. The use of topical anesthetics can help mitigate this. - Skin Type Considerations: Laser hair removal is most effective on individuals with light skin and dark hair due to the contrast in pigmentation. However, advancements in technology have made it possible for people with different skin tones and hair colours to benefit from the procedure. Conclusion Laser hair removal offers a convenient and effective solution for maintaining a hair-free bikini area. By understanding how the process works and what to expect, you can make an informed decision about whether it’s the right choice for you. Always consult with a qualified professional to ensure that you receive personalized care tailored to your needs. With the right approach, you can enjoy smooth, hair-free skin with minimal hassle!

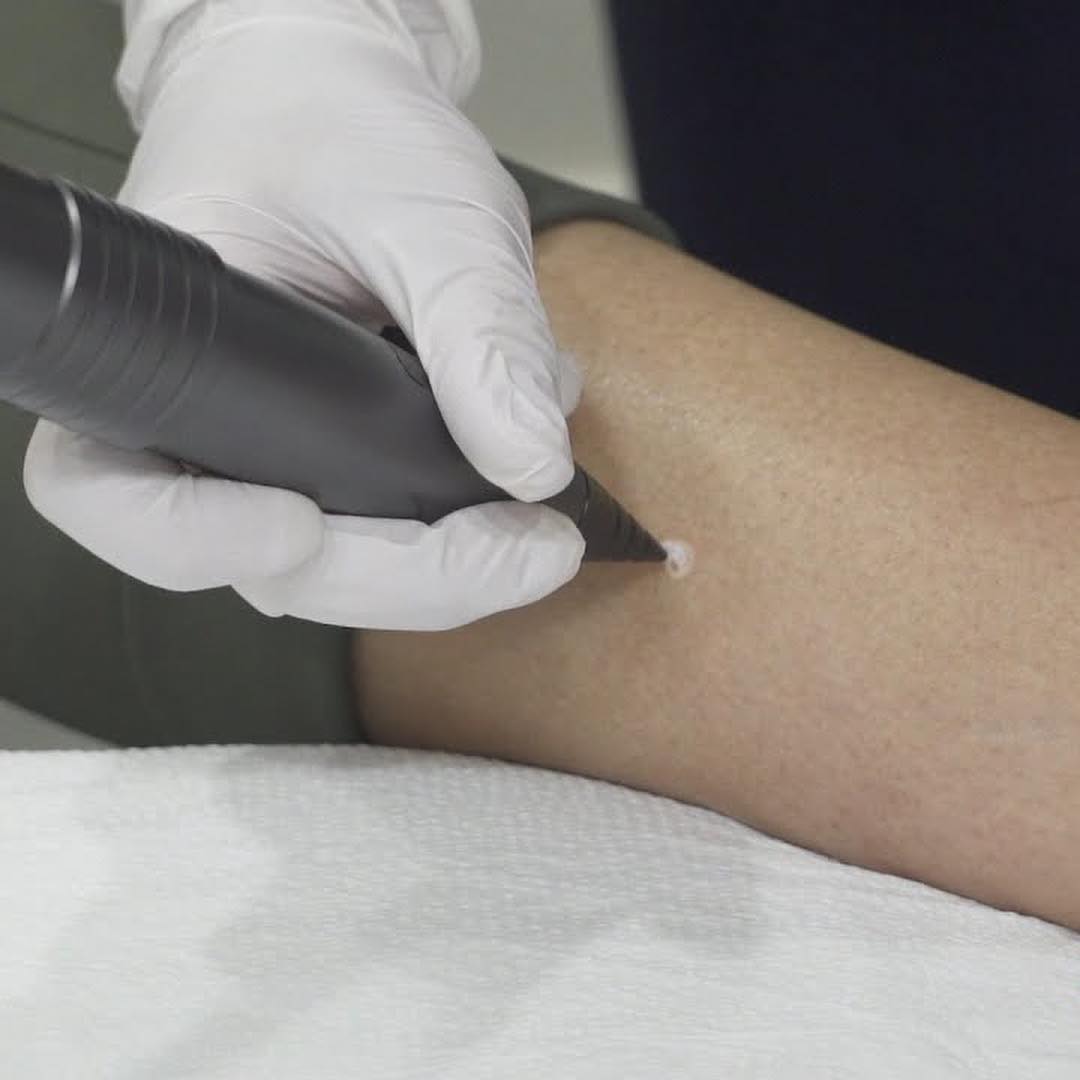
Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, are small, benign growths that often appear on areas of the skin where friction occurs, such as the neck, armpits, eyelids, and under the breasts. These soft, fleshy growths can vary in size, typically measuring a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters in diameter. Though they are harmless and generally do not cause any pain or discomfort, many people seek their removal for cosmetic reasons. How Do Skin Tags Form? Skin tags are formed when skin cells multiply and form a small flap of tissue. The exact cause of skin tags is not entirely understood, but several factors may contribute to their development: 1. Friction:Areas of the skin that experience frequent friction or rubbing against clothing or other skin can lead to the formation of skin tags. 2. Genetics: A family history of skin tags may increase the likelihood of developing them. 3. Hormonal Changes:Skin tags are commonly found in pregnant women or people with hormonal imbalances, suggesting that hormones might play a role in their formation. 4. Obesity:Increased weight can lead to skin folds, which may contribute to the occurrence of skin tags. 5. Age:Skin tags are more prevalent in older adults, likely due to the natural aging process of the skin. What is Cryotherapy? Cryotherapy is a medical treatment that involves the use of extreme cold to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue. When it comes to skin tag removal, cryotherapy is a popular and effective method. The procedure involves applying liquid nitrogen to the skin tag, which freezes the tissue. This freeze causes the skin tag to die and eventually fall off within a week or two. How Does Cryotherapy Work for Skin Tag Removal? 1. Consultation: Before the procedure, a healthcare professional will assess the skin tag and determine if cryotherapy is the appropriate treatment. 4. Application of Liquid Nitrogen:A spray device is used to apply liquid nitrogen directly to the skin tag. The extreme cold causes the water in the skin tag's cells to freeze, leading to cell death. 5.. Recovery:After the treatment, the skin tag will typically turn dark and fall off within a few days to two weeks. The surrounding skin may experience some redness and swelling, but these symptoms usually resolve quickly. Benefits of Cryotherapy for Skin Tag Removal - Quick and Painless:The procedure is relatively quick, often taking only a few minutes, and most patients report minimal discomfort. - Minimal Downtime:Cryotherapy does not require any significant recovery time, allowing patients to return to their daily activities almost immediately. - Effective Results:Cryotherapy is highly effective, with a high success rate in removing skin tags without scarring. Considerations and Aftercare While cryotherapy is generally safe, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing the treatment. They can provide guidance on what to expect and how to care for the treated area afterward. Aftercare typically includes keeping the area clean and avoiding sun exposure until it heals. Conclusion Cryotherapy is an effective and efficient method for removing skin tags, providing a quick solution for those seeking to enhance their skin's appearance. Understanding what skin tags are and how they form can help demystify this common skin condition. If you're considering skin tag removal, consult with a qualified professional to explore your options and find the best treatment for your needs.
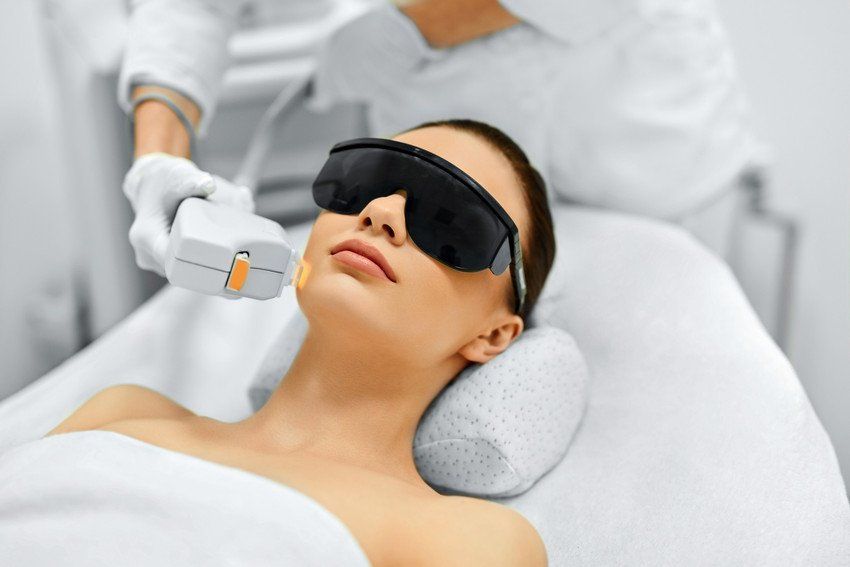
In the quest for smooth, hair-free skin, many people are turning to laser hair removal as a long-term solution. This popular cosmetic procedure offers a convenient and effective alternative to traditional hair removal methods like shaving, waxing, and plucking. If you're considering laser hair removal, it's essential to understand how it works and what you can expect from the experience. What is Laser Hair Removal? Laser hair removal is a medical procedure that uses concentrated beams of light (lasers) to target and destroy hair follicles. The process is designed to reduce or eliminate unwanted hair in various areas of the body, including the legs, underarms, bikini line, and face. How Does It Work? 1. The Science Behind It: The laser emits a specific wavelength of light that is absorbed by the pigment (melanin) in the hair. When the light is absorbed, it generates heat, which damages the hair follicle and inhibits future hair growth. This method is most effective on individuals with light skin and dark hair, as the contrast allows the laser to target the hair more effectively. 2. Pre-Treatment Preparation: Before undergoing laser hair removal, it's crucial to consult with a qualified professional. They will assess your skin type, hair color, and medical history to determine the best approach for you. Patients are usually advised to avoid sun exposure, waxing, and certain skin products in the weeks leading up to the treatment. 3. The Treatment Process: During the procedure, the technician will provide protective eyewear for you and themselves. A cooling gel may be applied to the treatment area to enhance comfort and protect the skin. The laser device is then applied to the skin, emitting pulses of light that may cause a sensation similar to a rubber band snapping against the skin. Sessions typically last from a few minutes to over an hour, depending on the size of the area being treated. 4. Post-Treatment Care: After the session, you may experience some redness or swelling in the treated area, similar to a mild sunburn. It's essential to follow your provider's post-care instructions, which may include applying soothing creams, avoiding sun exposure, and scheduling follow-up treatments. What to Expect from Laser Hair Removal - Multiple Sessions: Most people require multiple sessions (usually 4-6) to achieve optimal results. Hair grows in cycles, and the laser is most effective during the active growth phase. Treatments are typically spaced 4-6 weeks apart to target the hair at the right time. - Long-Lasting Results: Many individuals experience a significant reduction in hair growth after completing their sessions. While some hair may eventually regrow, it is usually finer and lighter in color. - Safety and Side Effects: Laser hair removal is considered safe when performed by a trained professional. Side effects are usually minimal and temporary, but it's essential to discuss any concerns with your provider beforehand. Conclusion Laser hair removal is an effective solution for those looking to simplify their hair removal routine. By understanding how the process works and what to expect, you can make an informed decision about whether it's the right choice for you. Always consult with a qualified professional to ensure the best possible experience and results. If you're ready to take the plunge into the world of laser hair removal, contact us today to schedule a consultation and start your journey to smooth, hair-free skin!
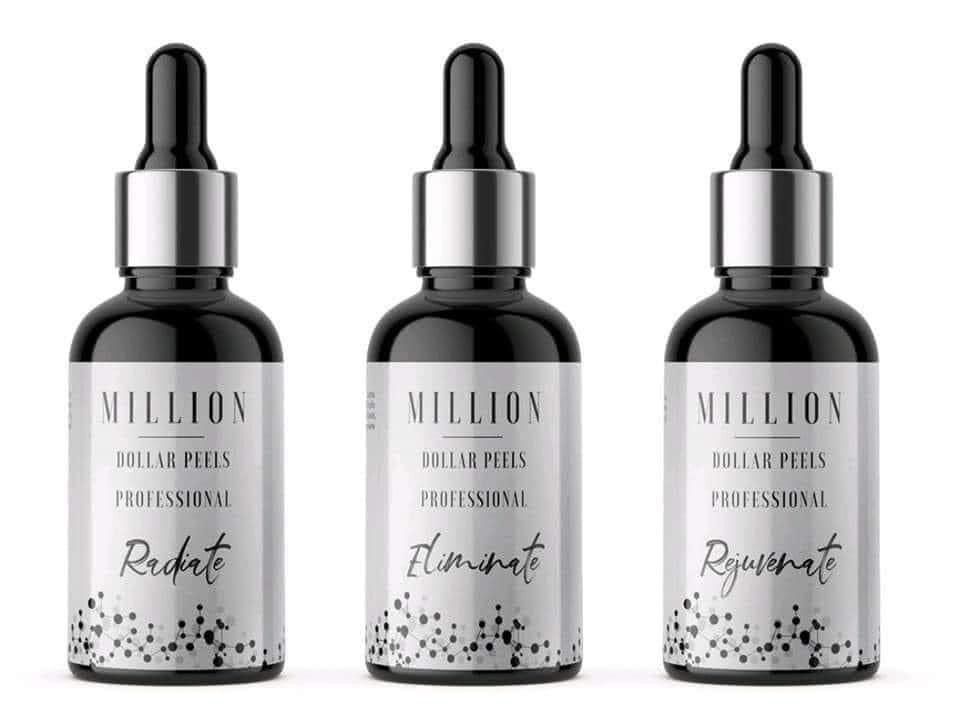

Look no further than the Million Dollar Immaculate Peels. These innovative chemical peels are designed to enhance and smooth the texture of your skin, making them an effective treatment for various skin concerns, including facial blemishes, wrinkles, uneven pigmentation, and problematic acne. What Are Million Dollar Immaculate Peels? The Million Dollar Immaculate Collection features three medium-depth skin peels that can be used individually or as part of a comprehensive treatment program at our clinic. These peels target issues related to uneven skin tone and the aging process, nproviding a pathway to healthier skin without the downtime typically associated with chemical peels. Who Can Benefit from This Treatment? The Million Dollar Immaculate Peels are perfect for anyone seeking near-instant results without the lengthy recovery periods. They are specifically formulated to support improvements for problematic, inflamed, and oily skin types. If you're struggling with irritation or breakouts, these peels can help calm, heal, and restore a balanced appearance. Explore the Benefits of Each Peel - Eliminate Peel:** Suitable for all skin types, this peel is perfect for those dealing with sensitive, problematic, dry, oily, or combination skin. It effectively calms and heals the skin, creating a healthy glow while addressing issues like active breakouts, blackheads, and rough texture. - Radiate Peel:** If uneven skin tone or pigmentation is your concern, the Radiate Peel is your go-to solution. This peel treats age spots, acne scarring, dullness, and photo-damage, leaving your skin with a post-treatment radiant glow. - Rejuvenate Peel:** Designed to combat the signs of aging, the Rejuvenate Peel improves fine lines, wrinkles, and dryness while restoring elasticity. Experience a more youthful complexion and defy the effects of stress on your skin. Treatment Details - Duration: 45 to 60 minutes - Price:65.00 - Recommended Frequency:Every 2 weeks for intensive treatment Contraindications to Consider Before undergoing treatment, please consult with us if you have any of the following conditions: - Under 18 years of age - Pregnant or breastfeeding - Irritated skin (sunburn, sores, lesions) - Skin conditions (eczema, psoriasis) - Recent use of prescription medications like Roaccutane (wait 12 months) - Localized skin infections (herpes simplex) - Keloidal or hypertrophic scarring - Blood disorders or clotting diseases - Diabetes (insurance and GP dependent) - High blood pressure or heart disease (insurance and GP dependent) - Skin cancer or undergoing cancer treatment - Autoimmune diseases (insurance and GP dependent) - Allergies to aspirin (salicylic acid) Essential Aftercare Instructions To ensure optimal results, follow these aftercare guidelines: - Apply SPF50 for sun protection - Avoid swimming for 7 days - Refrain from excessive exercise, heat treatments, or makeup for 48 hours - Do not exfoliate for 7 days post-treatment - Avoid other facial or body treatments for 2 weeks - Stay hydrated and avoid retinol products for 7 days before and after treatment Get in Touch Ready to rejuvenate your skin? Contact us today! 07966188645 info@harmonyclinic.org [ www.harmonyclinic.org ]( http://www.harmonyclinic.org ) Unit 10 Bridge & Ivy Farm, Lower Hacheston, Woodbridge, Suffolk, IP130AA Experience the transformation with Million Dollar Immaculate Peels and embrace the radiant skin you deserve!

Cryolipolysis, commonly known as fat freezing, is a popular non-invasive cosmetic procedure that helps reduce localised fat deposits. This innovative treatment uses controlled cooling to target and eliminate fat cells without harming the surrounding tissues. While it has gained popularity, it's essential to understand who the best candidates are for this procedure to ensure optimal results. Ideal Candidates 1. **Healthy Individuals**: The best candidates for cryolipolysis are individuals who are generally healthy and close to their ideal body weight. This procedure is not intended for significant weight loss but rather for contouring specific body areas. 2. **Localised Fat Deposits**: Cryolipolysis is most effective for individuals with stubborn fat deposits that are resistant to diet and exercise. Common target areas include the abdomen, thighs, flanks (love handles), back, and under the chin. 3. **Realistic Expectations**: Candidates should have realistic expectations about the results. While many experience noticeable fat reduction, it is not a solution for obesity or weight loss. Understanding that results can vary from person to person is crucial. 4. **Non-Smokers**: Non-smokers tend to heal better and have fewer complications post-procedure. Smoking can affect circulation and skin health, potentially impacting the results. 5. **Skin Tone and Elasticity**: Individuals with good skin elasticity and tone may see better results. Loose or sagging skin may not respond as well to the treatment, so it’s essential to have a consultation to evaluate skin condition. 6. **Age Considerations**: While there is no strict age limit, candidates should ideally be over the age of 18. Older adults often have different skin and fat characteristics, which can affect outcomes. Who Should Avoid Cryolipolysis? 1. **Obese Individuals**: Those with a body mass index (BMI) over 30 may not be suitable candidates, as cryolipolysis is not a weight-loss method. 2. **Certain Medical Conditions**: Individuals with specific medical conditions, such as cryoglobulinemia, cold agglutinin disease, or paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria, should avoid this treatment due to the risk of complications. 3. **Pregnant or Nursing Women**: While there is no evidence suggesting harm, it's generally recommended that pregnant or nursing women postpone elective procedures until after this period. 4. **Recent Surgery or Skin Conditions**: Candidates with recent surgeries in the areas of treatment or existing skin conditions (like rashes or infections) should wait until they are fully healed. Conclusion Cryolipolysis can be an effective solution for individuals looking to target stubborn fat without invasive surgery. However, the best candidates are those who are healthy, near their ideal weight, and have realistic expectations about the results. It’s vital to consult with a qualified professional to determine if this treatment is suitable for you. By understanding the criteria for candidacy, you can make an informed decision about whether fat freezing is the right choice for your body contouring goals.

What Are Skin Tags? Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, are small, benign growths that protrude from the skin's surface. They often appear as soft, fleshy lumps and can vary in size, typically measuring a few millimetre’s to a y. Skin tags are most commonly found in areas where the skin folds or rubs against itself, such as the neck, armpits, eyelids, and groin. Skin tags are composed of collagen fibres, blood vessels, and epithelial cells. While they are not harmful and do not typically require treatment, their presence can be bothersome for some individuals, particularly if they become irritated or snagged on clothing or jewellery. Who Is Prone to Skin Tags? Skin tags can occur in anyone, but certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing them: - Age: They are more common in adults, particularly those over 40. Obesity: Excess weight can lead to more skin folds, increasing the chances of skin tags. - Diabetes: People with diabetes are more susceptible to skin tags. Genetics: A family history of skin tags can also play a role in their development. What Is Cryotherapy? Cryotherapy is a medical treatment that involves using extreme cold to freeze and destroy abnormal tissue. It is commonly used in dermatology for various skin lesions, including warts, moles, and of course, skin tags. The most frequently used method for cryotherapy is liquid nitrogen, which is applied directly to the skin tag. The freezing process causes the cells of the skin tag to become damaged, leading to their eventual death and shedding. Cryotherapy is generally a quick procedure, often taking just a few minutes, and can be performed in a dermatologist's office. How to Remove Skin Tags Using Cryotherapy If you have skin tags that you wish to remove, here’s how cryotherapy typically works: 1. Consultation: First, schedule a consultation with a dermatologist. They will examine the skin tags to confirm they are benign and discuss your removal options. 2. Preparation: The area around the skin tag may be cleaned. 3. Application of Cryotherapy: The dermatologist will use a cryotherapy device to apply liquid nitrogen to the skin tag. This will freeze the tag, causing it to turn white and potentially feel a little cold or prickly. 4. Post-Treatment Care: After the procedure, the skin tag will gradually fall off within a few days to weeks as the tissue dies. You may be advised to keep the area clean and avoid picking at it. 5. Follow-up: While most skin tags can be removed in a single session, some may require additional treatments. Your dermatologist will schedule follow-ups as needed. Conclusion Skin tags are harmless growths that may be removed for cosmetic reasons or if they become irritating. Cryotherapy is a highly effective method for their removal, offering a quick and minimally invasive solution. If you are considering getting skin tags removed, consult with a dermatologist to explore the best options for your specific needs.

In today's world, body contouring and non-invasive fat reduction treatments have surged in popularity. Among these treatments, 3D Lipo stands out as an effective solution that combines several advanced techniques, including fat freezing, cavitation, radio frequency, and acoustic therapy. But what makes someone the ideal candidate for these services? Let's explore the key characteristics and considerations for individuals seeking to enhance their body shape and tone through 3D Lipo. Who is the Ideal Candidate? 1. Realistic Expectations: The first and foremost quality of an ideal candidate is having realistic expectations. While 3D Lipo can significantly reduce fat and improve skin tone, it is not a substitute for a healthy lifestyle or weight loss. Candidates should understand that results vary from person to person and that these treatments can complement, but not replace, a balanced diet and regular exercise. 2. Healthy Lifestyle: Individuals who maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, are more likely to benefit from 3D Lipo treatments. These services work best for those who are already close to their target weight but are struggling with specific areas of stubborn fat that do not respond to diet and exercise. 3. Targeted Problem Areas: Ideal candidates often have specific areas of concern, such as love handles, thighs, abdomen, or arms. 3D Lipo is designed to target localised fat deposits, making it perfect for individuals looking to refine their body contours. 4. Age Considerations: While there is no strict age limit for 3D Lipo treatments, candidates are typically adults. Younger individuals may have more elastic skin and may see better results, but older candidates can also benefit, especially with treatments that enhance skin tightness and elasticity. 5. Good Skin Condition: Candidates should have generally healthy skin, as the effectiveness of treatments like radio frequency and acoustic therapy relies on skin elasticity and condition. Individuals with chronic skin conditions or infections in the treatment area may need to consult with a medical professional before proceeding. 6. Not Pregnant or Nursing: Women who are pregnant or nursing should avoid these treatments, as hormonal changes can affect skin and fat properties, making results unpredictable. Understanding the Treatments - Fat Freezing (Cryolipolysis): This non-invasive procedure targets and eliminates stubborn fat cells by freezing them. It’s ideal for individuals looking to reduce localised fat without undergoing surgery. Cavitation: This technique uses ultrasound waves to break down fat cells, which are then naturally eliminated by the body. It’s particularly effective for smoothing out areas of uneven fat distribution. Radio Frequency: This treatment promotes collagen production and tightens the skin by delivering energy deep into the tissue. It’s excellent for candidates looking to improve skin texture and firmness. Acoustic Therapy: Utilising sound waves, this therapy enhances circulation and lymphatic drainage, helping to reduce cellulite and improve skin tone. Aftercare for Optimal Results Aftercare is crucial in maximising the benefits of 3D Lipo treatments. Here are some essential aftercare tips: 1. Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out the fat cells from the body and supports overall health. 2. Follow a Healthy Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains will complement the effects of the treatments. 3. Avoid Strenuous Exercise Immediately After Treatment: It’s advisable to refrain from heavy workouts for at least 24-48 hours post-treatment. Gentle activities like walking are encouraged to stimulate circulation. 4. Monitor Skin Condition: Keep an eye on the treated areas for any unusual reactions. If irritation or unexpected changes occur, consult your practitioner. 5. Regular Follow-Ups: Schedule follow-up appointments to assess progress and discuss any additional treatments that may enhance results. 6. Limit Sun Exposure: Protecting the treated areas from direct sunlight helps prevent skin irritation and promotes better healing. Conclusion The ideal candidate for 3D Lipo services is someone who is committed to a healthy lifestyle, has realistic expectations, and targets specific problem areas. With a blend of advanced techniques like fat freezing, cavitation, radio frequency, and acoustic therapy, candidates can achieve their desired body contours. Remember, the journey doesn’t end with the treatment; proper aftercare is essential for achieving and maintaining optimal results. If you’re considering 3D Lipo, consult with a professional to discuss your goals and determine the best approach for you.

In the quest for body sculpting and fat reduction, many individuals are exploring alternatives to traditional surgical procedures. One such method gaining popularity is cavitation, a non-invasive technique that promises to help individuals achieve their desired body shape without the risks and recovery associated with surgery. In this blog, we will delve into how cavitation works, its benefits, and why it may be a preferable option for many. What is Cavitation? Cavitation is a process that utilises ultrasound technology to target and break down fat cells in specific areas of the body. The procedure involves the use of a handheld device that emits ultrasound waves, creating microscopic bubbles in the liquid surrounding the fat cells. As these bubbles grow and collapse rapidly, they produce a wave of energy that disrupts the fat cell membranes, effectively liquefying them. The body then naturally processes and eliminates these broken-down fat cells through the lymphatic system. How Does Cavitation Work? 1. Ultrasound Waves: The cavitation device produces low-frequency ultrasound waves that penetrate the skin. These waves are specifically tuned to target fat cells while leaving other tissues unharmed. 2. Bubble Formation: The ultrasound waves cause the formation of small bubbles in the fat layer. As these bubbles expand and contract, they create a phenomenon known as cavitation. 3. Fat Cell Disruption: The bubbles imploding generate a shockwave that breaks down the structural integrity of the fat cells, turning them into a liquid form. 4. Natural Elimination: Once the fat cells are liquefied, the body’s lymphatic system takes over, gradually flushing out the released fat through natural metabolic processes. Benefits of Cavitation Over Surgical Procedures 1. Non-Invasive: Unlike surgical procedures such as liposuction, cavitation is non-invasive, meaning there are no incisions, stitches, or scars. This makes it an appealing option for those looking to avoid the risks associated with surgery. 2. Minimal Downtime: One of the most significant advantages of cavitation is the minimal downtime required. Many individuals can return to their daily activities immediately after the treatment, unlike surgical procedures that often require weeks of recovery. 3. Pain-Free Experience: Cavitation treatments are generally painless, with most patients experiencing only a mild warming sensation during the procedure. This contrasts sharply with the discomfort often associated with surgical fat removal methods. 4. Targeted Fat Reduction: Cavitation allows for targeted treatment of stubborn fat areas, such as the abdomen, thighs, and arms. This precision can lead to more aesthetically pleasing results compared to the more u approach of surgical options. 5. Cost-Effective: Generally, cavitation treatments are more affordable than surgical procedures. This makes it a viable option for individuals looking to manage their body shape without breaking the bank. 6. No Anaesthesia Required: Surgical procedures often require anaesthesia, which comes with its own set of risks and complications. Cavitation requires no anaesthesia, further reducing potential health risks. 7. Natural Results: The gradual fat reduction that cavitation provides can lead to more natural-looking results, avoiding the ‘overdone’ appearance that sometimes follows surgical interventions. Conclusion Cavitation offers a compelling alternative to traditional fat removal surgeries, combining effectiveness with convenience and safety. By understanding the mechanics of how cavitation works and acknowledging its benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their body sculpting options. If you're considering fat reduction treatments, consulting with a qualified professional about cavitation can help you determine if this non-surgical method aligns with your goals and lifestyle. As with any cosmetic procedure, it's essential to do thorough research and choose a reputable provider to ensure the best possible outcomes.